CADE usually employs the Finite Element Method (FEM) to undertake the simulation modelling and analysis of complex structural elements. Thus, this method is often used to analyse critical mechanical parts and elements, whose performance may be conditioned or influenced by other mechanical systems or elements.
In the railway sector and, more specifically, in the analysis of railway frame structures, the consideration of suspension systems (bogies) in its Finite Element Analysis becomes highly relevant: taking it into consideration may allow to characterise (in the most realistic way possible) the bogie rigidity transmitted to the frame structure, according to the requirements of the standard «UNE-EN 12663 (2014) Structural requirements of railway vehicle bodies».
The difference between implementing or not implementing the suspension system in the finite element analysis can be easily quantified. The results can be compared by analyzing the simulation of a multi-axle railway frame, applying the finite element method and using ANSYS software. For this purpose, two calculation models must be considered:
- Model implementing the suspension system.
- Model without implementation of the suspension system.
Results in the analysis of railway frame structures
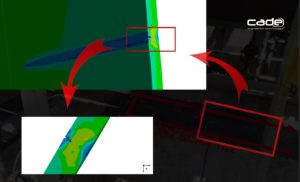
Equivalent von Mises stress (MPa)
Stress distribution in both calculation models analysed (with and without suspension system).
Model implementing the suspension system


Model without implementation of the suspension system


Considering that stress results are the most important indicators when validating a structure of this type, not to include bogies in finite element analysis might be a too conservative premise, from the structural integrity point of view, that may unnecessarily increase the material and manufacture costs.
Lineal buckling. First deformation mode (mm)
Modelo considerando el sistema de suspensión

| Modos | Factor pandeo |
| 1. | 9.81 |
| 2. | 10.55 |
| 3. | 11.45 |
| 4. | 14.92 |
| 5. | 17.11 |
| 6. | 17.37 |
| 7. | 17.76 |
| 8. | 17.81 |
| 9. | 18.02 |
| 10. | 18.06 |
Modelo SIN considerar el sistema de suspensión

| Modos | Factor pandeo |
| 1. | 13.45 |
| 2. | 16.95 |
| 3. | 17.19 |
| 4. | 17.28 |
| 5. | 17.38 |
| 6. | 17.55 |
| 7. | 17.62 |
| 8. | 17.66 |
| 9. | 17.89 |
| 10. | 19.01 |
Continuing with the comparative results and observing the deformation modes and buckling factors, it appears that the implementation of bogies in the finite element analysis provides higher safety factors against buckling. In fact, considering the suspension system in the model allows to identify buckling modes that cannot be identified in finite element models without it. When the suspension system is not considered, the direct application of boundary conditions on the frame stiffens the model, generating hardly conservative safety values against buckling and showing fictitious failure modes.
Conclusions of the analysis of railway frames with and without bogies
In conclusion, by considering bogies in railway frames validation, CADE achieves:
- To lighten railway structures, reducing material and manufacturing costs.
- To obtain safer railway structures, because it is possible to identify buckling modes (not found with finite element analysis without bogies consideration) and at the same time, to obtain higher safety factors against buckling.
What is a suspensions system (bogie)?
The suspension system consists of a primary suspension (which transmits efforts between the wheels and the bogie) and a secondary suspension (which is responsible for transmitting the efforts between the bogie and the frame of the railway vehicle).
Both suspensions consist of a series of springs and shock absorbers that allow to transmit efforts between the wheels, the bogie and the railway frame.


Experts in Analysis and Simulation
CADE is specialized in mechanical and industrial engineering, being a pioneer in the use of applications of computer-aided engineering (CAE) for solutions in Oil&Gas and Power Generation Industry, among other industries. Therefore, with more than 15 years of experience, CADE provides simulation modelling, engineering and consulting services, finite element analysis (FEA) and computational fluid dynamics (CFD) in equipment, high pressure ducts and non-conventional structures.
Further information about finite element analysis and simulation modelling in railway frames:
For any further information about advanced engineering services of design and consultancy for railway frames, you can contact us on +34 967 19 01 72, email cade@cadesoluciones.com or complete the form bellow: